Importance of Initial Process Studies for PPAP
Initial Process Studies used for to measure the consistency of the process or product performance based on specified design by reaching consistency of the product quality and performance. Initial Process Studies helps to manufacturers to reduce wastages, reworks, over processing. Involvement of control chart disclose the status of process performance and product quality to manufactures by real time consideration of SPC (Statistical Process Control). Whether manufacture choosing real time Initial Process Studies can avoid and control the special cause variation on process and product. Moreover can focus on process improvements and defect free products.
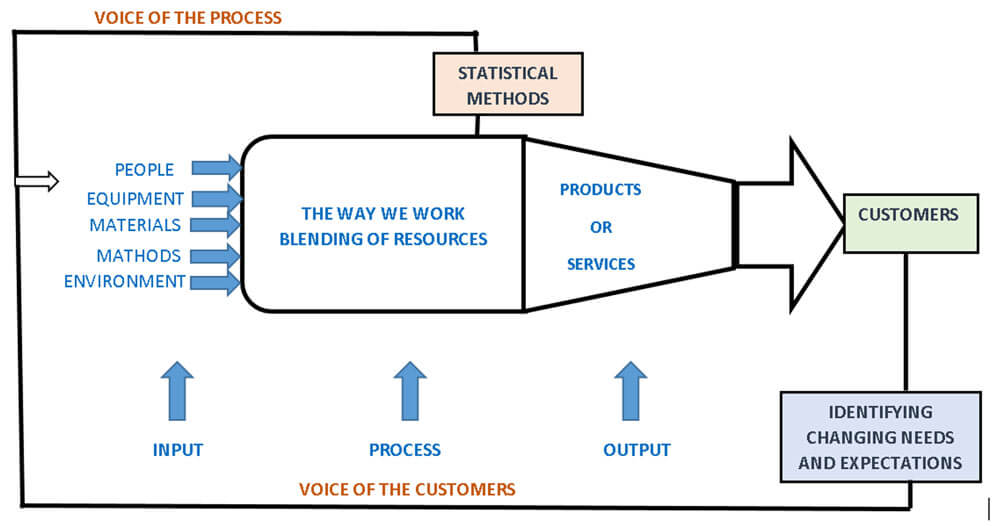
PPAP Process Model with feedback:
Initial Process Studies:
Initial Process Studies is the application of statistical techniques to determine whether the output of the process confirms to the products of service designs.
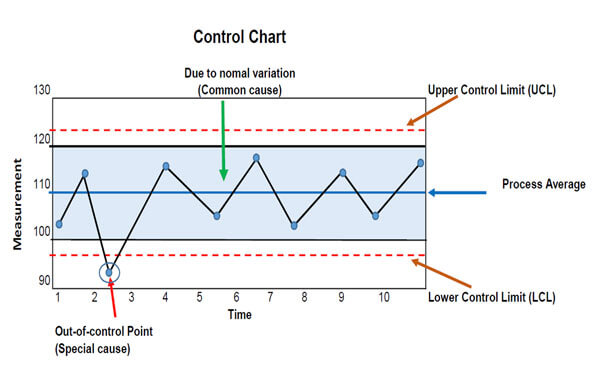
A process is in control if:
- No sample points outside limits.
- Most points near process average.
- About equal number of points above and below centerline.
- Points appears randomly distributed.
Initial process Studies:
- Purpose is to determine if production process is likely to produce a product that meet customer requirements
- Initial process capability and performance to be determined for all special characteristics designated by customer or organization
- Customer concurrence to be obtained on Indices for estimating process capability prior to submission ( Cpk, Ppk).
- Initial studies focus on variables and not attribute data
- May be replaced by long term historical data from similar process- customer concurrence needed
- For bulk material – customer agreement required
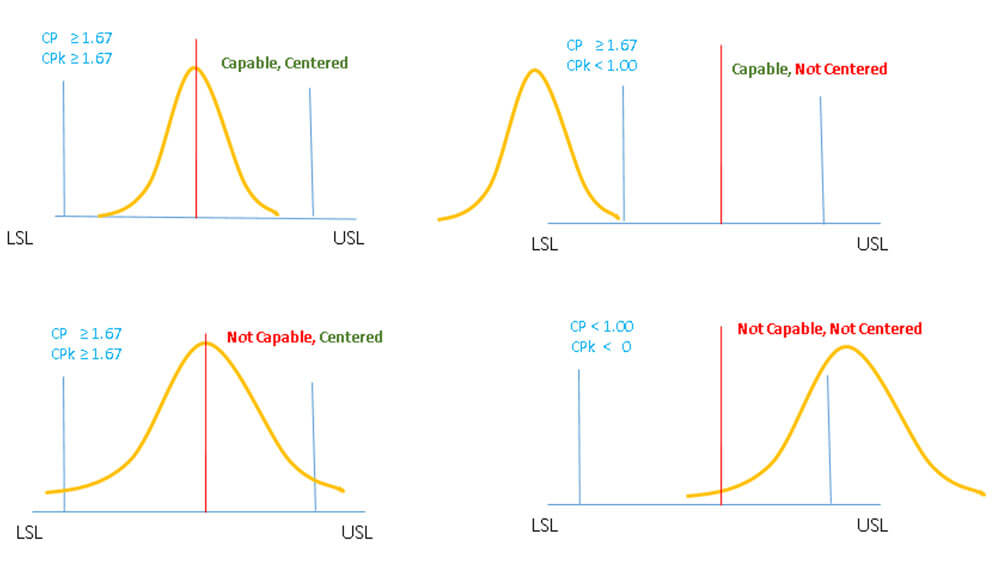
- Index>1.67-acceptable
- For Index between 1.67 and 1.33, customer agreement needed
- Index <1.33 currently not acceptable.
- Initial process capability acceptance criteria is only one of a number of requirements that leads to PPAP approval
Process Capability:
Calculate the appropriate statistical metrics in order to determine how the “Voice of the Process” compares to the “Voice of the Customer.”
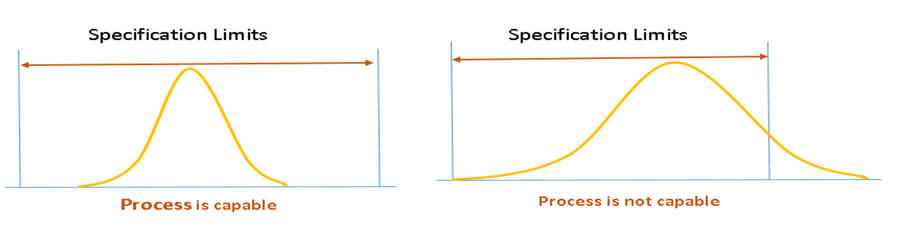
Capability Indices:
- Cp – Relates short term (within subgroup) standard deviation to tolerance. Sometimes called “Entitlement,” meaning it is the best the current process can do, if centered
- Cpk – Relates short-term mean & short term (within subgroup) standard deviation to tolerance. Only tells you about the nearest spec limit; doesn’t tell anything about the other side
- Pp- Relates long term (overall) standard deviation to tolerance
- Ppk – Relates mean & long term (overall) standard deviation to tolerance
- Only tells you about the nearest spec limit; does not tell anything about the other side
Difference between Cp & Cpk:
- Cp – Determines capability of producing to specification
- Cpk – Same as Cp, but also measures how centered the process is
- It is important to look at both!
Cpk predicts capability
- Based on short term within subgroup variation
- Does not include the effect of process variability between subgroups
Cpk should be used when:
- Developing new parts
- Revising specifications on a part
- Materials, processes, manufacturing location, or equipment have significantly changed
- Material suppliers have changed (include certificate of analysis)
Ppk indicates past performance:
- Based on long term total variation
- Unlike Cpk, Ppk is not limited to variation within subgroups
- However, Ppk cannot isolate within subgroup variation from between subgroup variation
- When calculated from the same data set, Cpk and Ppk can be compared to analyze the sources of process variation
Ppk should be used when:
- The supplier is new to customer , but has already been manufacturing a part
- The supplier is existing, but has produced a number of nonconforming parts