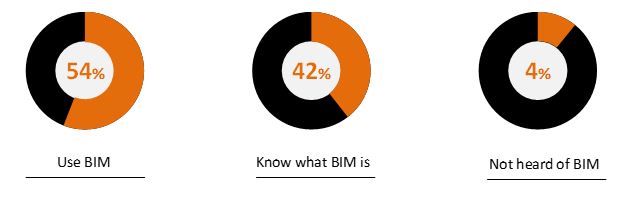
54% of the Industry believes BIM is the way forward in Building Engineering.
 “BIM or Building Information Modelling is a process for creating and managing information on a construction project across the project lifecycle”.
BIM has been around since the introduction of computing. As early as 1957, a computer-aided machining (CAM) software, known as Pronto, was designed for commercial purposes. However, it was not until 1977 that Charles Eastman designed the first CAD program to possess a modern BIM platform. The use of BIM was not very popular until the year 2002 when Autodesk and other software got involved in the field and came up with the present-day 3D plans.
“BIM or Building Information Modelling is a process for creating and managing information on a construction project across the project lifecycle”.
BIM has been around since the introduction of computing. As early as 1957, a computer-aided machining (CAM) software, known as Pronto, was designed for commercial purposes. However, it was not until 1977 that Charles Eastman designed the first CAD program to possess a modern BIM platform. The use of BIM was not very popular until the year 2002 when Autodesk and other software got involved in the field and came up with the present-day 3D plans.
The Growth of BIM can be explained by the following Technical possibilities:
- Added Dimensions: This feature enables work to be done in three dimensions in addition to cost and time dimensions. It is possible to view cost estimations and the bills of materials as work is being done on a design. Most importantly, it allows the preparation of time schedules which can be adhered to in order to achieve efficiency.
- Virtual Information Model: Designers can share a project’s virtual information model with principal and sub-contractors as well as the operators or owners of the facility. This feature ensures that information loss during the period of sharing between stakeholders is kept to the barest minimum. Owners of complex structures can take advantage of a more extensive information database.
- All Encompassing System: Every single process like project management, cost management, facility operation, among others is supported by BIM. In simple terms, BIM is useful throughout a building’s life cycle.
- BIM Management: The purpose of this feature is to manage information systems efficiently all through the life cycle of a project. It supports the tracking of an object-oriented BIM against any performance objectives which the stakeholders set.
- Capture Reality: BIM offers more than paper does in the way it captures reality and streamline project preparations. Mapping tools combined with images of Earth makes it possible to access aerial imagery, digital elevation among other things.
- Maintain Control: With the provision of features such as auto-save and connections, it is possible to project history which reveals how much time was spent working on a model. This eliminates the corruption of files as well as its disappearance.
- Improve Collaboration: Sharing models is a breeze with BIM compared to drawing sets. This enhances collaboration through the use of tools designed for different disciplines. As a result, everyone has a chance of making an input towards the design of a project before it is finalized.
- Processes: It offers an increased speed and efficiency in the way things are done. For instance, it is so much easier to create spaces automatically from Excel to BIM Revit.
- Policies: There will be a need to protect companies as they share information. This will enhance collaboration between stakeholders. It could be through the use of an electronic release form or an application of filters to any information which is shared. The tactic will minimize risk while the workflows that BIM relies on are streamlined.
- People: For change to be adopted, the people involved have to be on board. To make good use of the technology offered by BIM, strong in-person relationships have to be built. To avoid the risk of obsolescence, new technology needs to be embraced in addition to a willingness to learn it. BIM will encourage innovation and investment in training, education, and development.